Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the C if statement to execute a block of code based on a condition.
Introduction to the C if statement
The if statement allows you to run a block of code based on a condition. The syntax of the if statement is as follows:
if(expression)
statement;Code language: C++ (cpp)The if statement evaluates the expression. If the expression evaluates to true (or non-zero value), the if statement will execute the statement.
However, if the expression evaluates to false (or zero), the if statement will not execute the statement and passes the control to the statement that follows it.
Note that C treats 0 as false and a non-zero value as true.
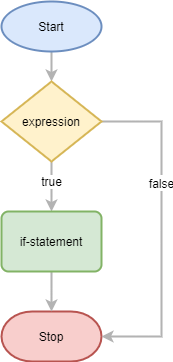
The following flowchart illustrates how the if statement works:
The following example uses the if statement to display a message to the screen if the age is greater than 16:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main()
{
int age = 18;
if (age > 16)
printf("You can drive.");
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Since the age is 18, you’ll see the following message in the output:
Code language: C++ (cpp)You can drive.
To form a complex condition, you can use the logical operators, including logical AND operator, logical OR operator, and logical NOT operator.
The following example uses an if statement with a compound condition:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main()
{
int age = 18;
bool have_driving_license = true;
if (age > 16 && have_driving_license)
printf("You can drive.");
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Since the age is 18 and the have_driving_license is true, you’ll see the following message in the output:
Code language: C++ (cpp)You can drive.
If you change the age to a value that is less than 16 or the have_driving_license to false, you won’t see anything in the output.
Using the if statement to execute multiple statements
To execute multiple statements baed on a condition, you use the following if statement:
if (expression)
{
statement 1;
statement 2;
// ...
}Code language: C++ (cpp)In this syntax, you wrap the statements in the curly braces ({}).
The following example uses an if statement to execute multiple statements:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age = 18;
if (age > 16)
{
printf("You can drive.\n");
printf("You can apply for a passport.\n");
printf("You can register to vote.\n");
}
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Since the age is greater than 16, you’ll see the following in the output:
Code language: plaintext (plaintext)You can drive. You can apply for a passport. You can register to vote.
Note that there’s no semicolon at the end of the if statement like this:
if (expression);
{
statement 1;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)If you place the semicolon (;) like above, the statements in the block that follows the if statement will always execute.
The reason is that C will treat this code as an if statement without a body:
if (expression);Code language: C++ (cpp)and a block:
{
statement 1;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)And that block doesn’t depend on the if statement above.
Summary
- Use the C if statement to execute one or more statements based on a condition.